The Grid of the Future: Renewable storage systems
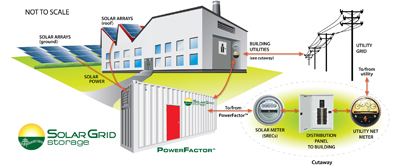 Over the last 15 years, renewable energy companies have focused on technological and financial innovations to enable cost-effective deployment of renewables—primarily for solar and wind power projects. The goal in most any case: to generate and supply safe, clean, and reliable power in an efficient and cost-effective manner.
Over the last 15 years, renewable energy companies have focused on technological and financial innovations to enable cost-effective deployment of renewables—primarily for solar and wind power projects. The goal in most any case: to generate and supply safe, clean, and reliable power in an efficient and cost-effective manner.
However, as extreme weather events continue to break out across the globe, and with terrorist threats a modern day concern, there’s growing unease about the electrical grid’s vulnerability. Superstorm Sandy was a wake-up call for many in the United States. In its grim aftermath, millions of residents and businesses in the Northeast lost power, and the public came to appreciate the need for an upgraded, more resilient infrastructure.
In the immediate future, one critical consideration will be how quickly it’s possible to create that desired resiliency. A move away from central power plants, by adding smaller more distributed generation that can be built more quickly—including for solar and wind power—is a step in the right direction. Pairing solar generation with storage offers a giant leap toward a smarter, more efficient electrical grid, which can deliver clean power on an unprecedented scale.
And, perhaps, an added benefit is that when renewables are paired with storage, solar and/or wind energy not only provides a buffer to intermittency issues, but also provides a foundation and a need for a variety of other valuable grid services that can help maintain grid stability.
Providing value the grid
New Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) Orders 755 and 784 require utilities and grid operators to develop programs aimed at properly valuing fast-reacting technologies, such as batteries that help balance power on the grid. These technologies will make the grid more resilient and make the energy supply more reliable, efficient, and renewably sourced. Adding storage to the tens of thousands of solar projects already installed, and accelerating the deployment of new storage-integrated installations, provides resiliency and added value to the power grid.
Typically, solar photovoltaic (PV) systems are designed to shutdown when utility power is interrupted. But, when PV systems are paired with storage, they can generate power during outages—and store energy for use at night. A properly designed PV and storage system can provide critical emergency power indefinitely. This is something millions of Americans would have welcomed after Superstorm Sandy, not to mention during the massive snowstorms that hit many states quite hard this winter.
Adopting storage solutions
Deploying PV and storage at emergency service venues would clearly benefit communities in the wake of natural disasters, and several utilities and pioneering project developers/integrators have already begun delivering solar storage projects for emergency backup power.
Former FERC chairman Jon Wellinghoff and Maryland governor Martin O’Malley are among the many visionary leaders who have advocated pairing clean generation with storage. Many other governors, along with regulators and policymakers Democratic and Republican alike, are striving to make renewable energy a more integral part of America’s energy portfolio.
In New Jersey, for example, where this effort has been a bipartisan affair over the last 12 years, solar deployment now stands at more than one gigawatt, with more than 25,000 installations and growing.
Policymakers, elected officials, and regulators have the potential to make a positive impact on their states—indeed, on the entire globe—by making PV and storage a priority. Even on an individual level, renewable storage solutions benefit electricity customers by reducing and stabilizing utility bills. Furthermore, PV and storage multiplies solar investments by helping operators use battery storage 24 hours a day to help balance power on the grid. With the bundle of benefits it offers, PV and storage has already begun to transform the grid of the future.
Much like the falling solar costs in recent years, storage technology costs are also dropping, spurring wider adoption of renewables and battery storage solutions. Plus, new business models are empowering integrators and engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) companies to outfit hospitals, schools, shelters, gas stations, and emergency centers with PV and storage in a cost-effective manner.
By creating effective public-private partnerships that supports the technology, leaders can ensure that homes, businesses, and government facilities are not only energy efficient, but also more resilient should disaster hit.
Final thoughts
Just this past December, the US Energy Department released a report on grid energy storage, noting that “energy storage is a vital component of a more resilient, reliable and efficient electric grid.”* The report also identified four challenges that must be addressed to enable energy storage: the development of cost-effective energy storage technologies; validated reliability and safety; an equitable regulatory environment; and industry acceptance.
As the nation continues taking steps toward a robust, reliable electrical grid, it’s important to urge leaders to truly focus on clean and reliable solar energy that has integrated storage capacity. Advocates believe it’s crucial for the US to accelerate the use of affordable, reliable solar power, and to upgrade the utility grid by making it more resilient during power outages.
Investing in solar and innovative storage technology certainly goes hand-in-hand with economic development, job creation, smart grid deployment, and sound environmental policy. This would also set an example for the rest of the world—and improve the quality of life for generations to come.
* Download the report at: http://energy.gov/node/778601
Tom Leyden is the CEO of Solar Grid Storage, headquartered at the Philadelphia Navy Yard.
Solar Grid Storage
http://solargridstorage.com
Author: Tom Leyden
Volume: March/April 2014












